How to Read Your Driving Licence
Back in the day, driving licences were different from how they are today and came a long way since.
In 1903 the “Motor Car Act” was introduced in the UK, requiring all car owners to register their vehicles with their local borough council and stipulating that holders of a sulphur-yellow document were allowed to drive a car or motorcycle. The licence back then was fabric-bound and similar to today’s passports; you could buy it for 5 shillings and no test was required.
In 1930 vehicle classes were added so that authorities knew exactly what vehicle was an individual able to drive.
In 1934 as part of the Motor Vehicles Regulation, competency driving tests and penalties for reckless drivers were introduced.
Up until 1973, driving licences were issued by local authorities and needed to be renewed every three years. However, in the mid-70s it was agreed that a licencing body should have been put in place to make the process smoother and easier to keep under control. This is when the Swansea headquarter of the DVLA (Driver and Vehicle Licensing Agency) was born.
Fast forward to 1999, the thick plastic Photocard was introduced to give the DVLA more accurate information about a driver’s identity, as well as helping the police fight car-related crimes. This would have (and still does) allowed Police to establish the driver’s identity if the latter was pulled over.
Initially and before digitisation, the Photocard licence came together with a paper counterpart with the details of one’s penalty points and disqualification periods, whereas now, in 2022, through one’s Photocard licence, authorities will be able to consult records and one’s driving history in one click.
But what do all the different sections on a Photocard driving licence mean? If you have ever been curious then you’re in the right place.

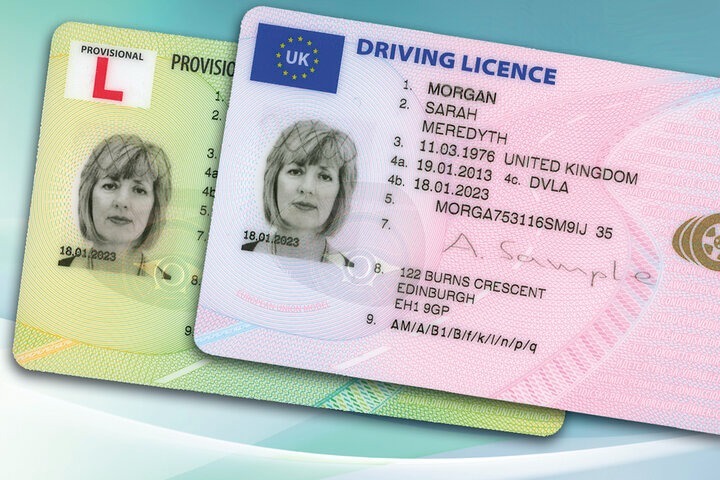
At the front of your licence there are 9 sections.
Personal Details
Section 1: Your surname
Section 2: Your first and middle name
Section 3: Your date of birth and place of birth
Issue Details and Validity
Section 4a: This is the date from when your driving licence is valid
Section 4b: This is the date until which your driving licence is valid (you will need to renew it before it expires, so always keep an eye on the date!)
Section 4c: Who issued your driving licence/issuing authority
Section 5: This is your driving licence number; it is unique to you and includes a combination of numbers and letters
Section 7: Your signature
Section 8: Your address (always remember to change the address on your driving licence if you are permanently moving from one address to another)
Section 9: These are the categories of vehicles you are permitted to drive (if you see at the back of your driving licence, there are going to be more details concerning these categories)
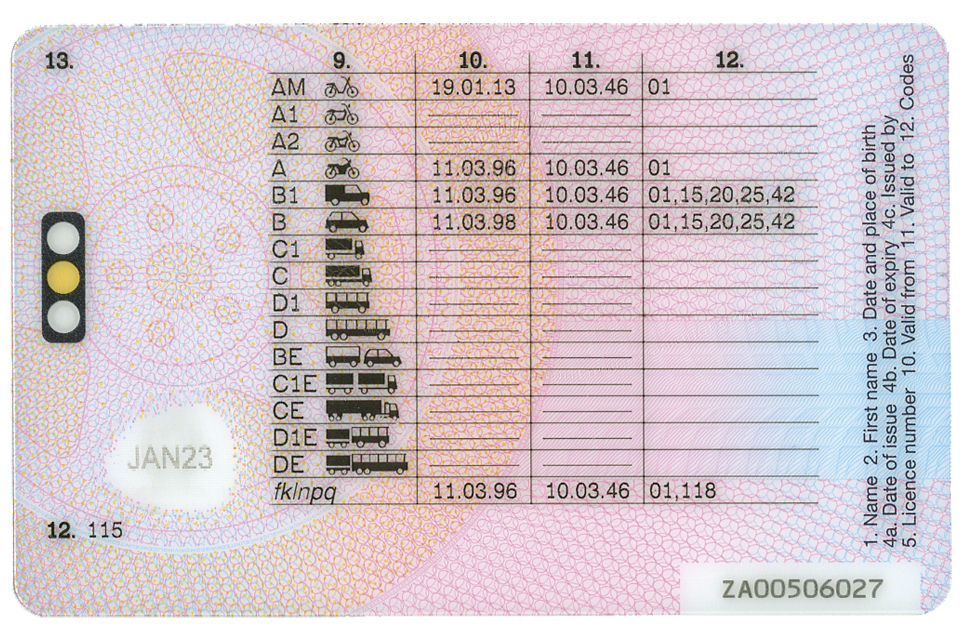
At the back of your licence there are 4 columns.
Column 9 lists the types of vehicle you are allowed to drive
Columns 10 and 11 respectively list from and until when you are allowed to drive vehicles in that particular category
Column 12 lists any limitation you may have which is specific to that category
What Licence Categories Apply to Motorbikes?
AM: This category applies to mopeds, allowing the licence holder to drive two-wheeled or three-wheeled vehicles at a maximum speed of 28mph (this also includes quad bikes). You need to be at least 16 years old to hold an AM licence and have passed your motorbike theory and practical test.
A1: Allows you to drive motorbikes with an engine of up to 125cc with a power input up to 11kW, and tricycles with a power input up to 15kW. To hold an A1 licence, you need to be at least 17 years old and have passed your motorbike theory and practical test.
A2: This licence category applies to motorbikes up to 35kW and you will need to be at least 19 years old to take your theory and practical test.
A: Represents the “highest” degree of motorbike licences, allowing riders to drive any bike of any size or engine. You will need to either be 24 years old to get this licence or 21 years old if you’ve held your A2 licence for more than 2 years and have passed both your motorbike theory and practice test.
What Licence Categories Apply to Cars?
B1: Allows you to drive a vehicle with 4 wheels up to 400kg unladen or 550kg if designed for carrying goods. It only requires a driver to have passed a standard driving theory and practice test.
B: This licence category allows you to drive a manual or automatic car, or both, depending on which driving test you’ve passed.

What Licence Categories Apply to Lorries and Buses?
C1: Allows you to drive vehicles between 3,500 and 7,500kg maximum authorised mass (MAM) (with a trailer up to 750kg)
C: This licence lets you to drive any vehicle over 3,500 kg (with a trailer up to 750kg MAM)
You will need to hold a standard driving licence for both of these categories, but you will also have to have applied for a provisional lorry licence beforehand.
D1: Allows you to drive minibuses with no more than 16 passenger seats, a maximum length of 8 metres and a trailer up to 750kg.
D: This licence allows you to drive any bus with more than 8 passenger seats and a trailer up to 750kg.
What Licences Apply to Trailers?
BE: Is a bit of a particular licence category as it has recently gone through an update on the 16th December 2021, allowing drivers who passed their driving test after 1st January 1997 to be able to tow trailers up to 3,500 kg MAM with a standard driving licence and without the need of passing any additional tests or qualifications.
C1E: Allows drivers to drive C1 vehicles with a trailer of over 750 kg, however, the combined weight can’t exceed 12,000kg MAM.
CE: This category is the same as Category C apart from the fact that it allows you to tow a trailer over 750kg.
D1E: Allows you to drive D1 minibuses and tow a trailer over 750kg with a weight not exceeding 12,000kg MAM.
DE: Very similar to the previous category, this licence allows you to drive buses seating more than 8 passengers together with towing a trailer over 750kg.

Are There Any Other Licence Categories?
Yes, there are several other categories to encompass all types of vehicles. The most popular are the following:
f: Allows you to drive any agricultural tractor.
k: Allows you to drive mowing machines or a pedestrian controlled vehicle like a Segway.
q: Allows you to drive two and three-wheeled vehicles without pedals, although their engine mustn’t be more than 50cc and the maximum speed cannot exceed 15 mph.
What Are the Most Common Driving Limitations?
Earlier we were talking about driving limitations that can appear on your driving licence, they can be category specific and appear in the form of a “driving licence code”. Let’s have a look at the most common ones.
01 – Eyesight correction (i.e. the use of glasses whilst driving)
02 – Hearing Aid
40 – Modified Steering
78 – Restricted to automatic transmission vehicles
105 – Vehicle no more than 5.5m long
115 – Organ donor
We hope that this article has helped you clarify some driving licence sections which may appear obscure to many. If you would like to know more about driving licence codes, don’t forget to visit the DVLA website.

Tags: *DVLA *Driving_Licence *Driving *Licence *Photocard